VISIR-2 is an open-source, Python-coded numerical modelling framework for ship voyage optimisation or weather routing.
Leveraging a graph-search methodology, VISIR-2 makes use of dynamic meteo-oceanographic fields to compute optimal ship routes. Its versatility extends to navigating coastal and archipelagic regions. The model and its accompanying software are comprehensively documented in several peer-reviewed publications.
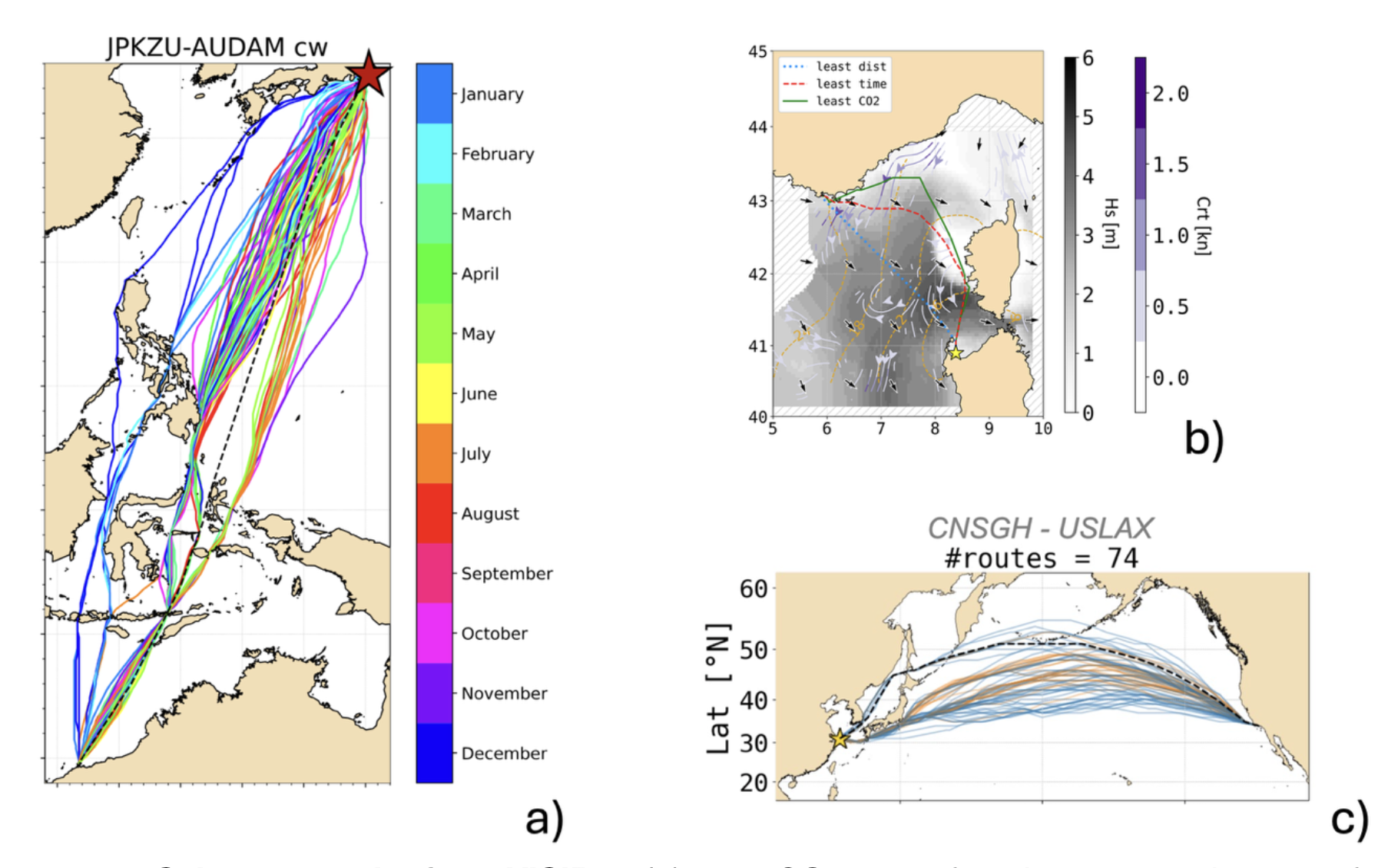 Figure 1. Selected results from VISIR-2: (a) least-CO₂ routes for a bulk carrier departing from Kisarazu (Japan) throughout 2021; (b) three types of optimal routes for a ferry departing from Porto Torres (Italy) on January 9, 2022; (c) Year 2024’s least-CO₂ routes for a container ship on the green corridor between Shanghai (China) and Los Angeles/Long Beach (USA). For all routes, both waves and surface ocean currents were considered.
Figure 1. Selected results from VISIR-2: (a) least-CO₂ routes for a bulk carrier departing from Kisarazu (Japan) throughout 2021; (b) three types of optimal routes for a ferry departing from Porto Torres (Italy) on January 9, 2022; (c) Year 2024’s least-CO₂ routes for a container ship on the green corridor between Shanghai (China) and Los Angeles/Long Beach (USA). For all routes, both waves and surface ocean currents were considered.
As of June 2025, the VISIR-2 model powers multiple operational services: GUTTA-VISIR, delivering least-CO₂ routing for ferries, and FRAME-VISIR, tailored for leisure boats—both active in the Adriatic and Norther Ionian Seas. In addition, VISIR-2 supports a Docker-based service for ocean-going vessels along the Pacific Green Corridor, as part of the European Digital Twin of the Ocean initiative.
Note: The Matlab-coded VISIR-1 model used to power a service (VISIR-nav) for on-demand route optimization in the Mediterranean Sea.
Resources: